Now also free widgets
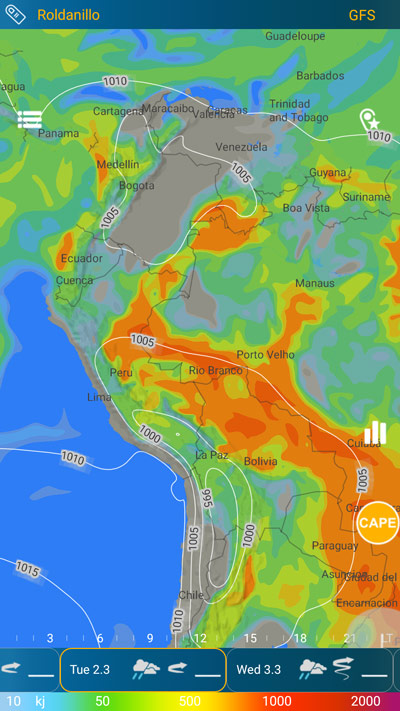
The CAPE (Convective Available Potential Energy) index is a meteorological indicator used to assess the potential for convective development and thunderstorm activity in the atmosphere. It measures the amount of energy available for vertical air ascent and the formation of convective clouds.
The CAPE index quantifies the vertical stability of the atmosphere and the temperature difference between the Earth's surface and higher atmospheric layers. Higher CAPE values typically indicate a greater potential for convective updrafts and the development of thunderstorms.
In the context of aviation, the CAPE index is an important factor that pilots and paragliders consider when planning their flights. Higher CAPE values suggest favorable thermal conditions for aircraft and paragliders, indicating a higher likelihood of thermal updrafts and the possibility of longer and higher flights. Conversely, lower CAPE values may indicate reduced potential for thermal activities and limited flying opportunities.
